~{→看不见LaTex格式的Dalao们请刷新本页Thanks♪(・ω・)ノ←}~
#.Maze
题面
A maze is represented by a tree (an undirected graph, where exactly one way exists between each pair of vertices). In the maze the entrance vertex and the exit vertex are chosen with some probability. The exit from the maze is sought by Deep First Search. If there are several possible ways to move, the move is chosen equiprobably. Consider the
following pseudo-code:
1 | DFS(x) |
$V(x)$ is the list vertices adjacent to $x$. The $flag$ array is initially filled as FALSE. $DFS$ initially starts with a parameter of an entrance vertex. When the search is finished, variable $count$ will contain the number of moves.
简要翻译
一棵 $n$ 个点的树,起点和终点随机选取。运行如下程序, $V(x)$ 是与 $x$ 相邻的顶点列表,最初 $flag$ 数组为 $false$,$DFS$ 的参数是起点,你要求 $count$ 的期望值。
(自己给洛谷的翻译跪着也要搬过来)
Input
第一行一个数 $n$,表示个节点。
接下来 $n-1$ 行,每行两个数$(u,v)$,表示有一条从 $u$,到$v$的无向边。
然后是$n$行,每行描述一个节点表示该节点被选为进入点的 $x$ 和该节点被选为离开的 $y$ 。
此处的x和y用于求每个点被选为进入点的概率和被选为离开点的概率,即:
$p[x]=\frac{x}{sum(x)}$,$p[y]=\frac{y}{sum(y)}$.
Output
一个实数表示$count$的期望。
(误差允许范围$\le 10^9$)
Sample Input 1
2
1 2
0 1
1 0
Sample Output 1
1.00000000000000000000
Sample Input 2
3
1 2
1 3
1 0
0 2
0 3
Sample Output 2
2.00000000000000000000
Sample Input 3
7
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
3 6
3 7
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
Sample Output 3
4.04081632653
Hint
$n<10^5$
突然发现这是一道比较经典的题,讲课时被提到了好几次,我神奇般的给了某谷一个强有力的翻译,不扯了(竟然知道在扯)。
看过随机树那篇题解的都知道。(又骗人去刷博客访问量)
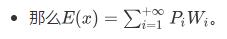
(原谅我直接截图)
题面非常的显然,那么我们先求出每一棵子树的大小,设一个$P_x$表示当$x$被当做离开点时,从别的子树出发到达他的概率。
使用$DFS$求出子树大小,同时求出该子树中每个点被选为$Enter$的概率和,并且枚举每个点作为$Exit$。
用之前的那个公式求出以该节点为根节点的子树出发到该节点的期望以及从别的子树出发到该节点的期望。
设这个点为$x$,对于它以外的子树将其看作$x$的另一子树。
这样一设计,这题似乎就可以Van爆了。
Code
1 |
|